BJT and MOSFET are two types of semiconductor transistors. Even though both of them are transistors, they are different from each other in various aspects. By the end of this article, you will know the difference between BJT and MOSFET.
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
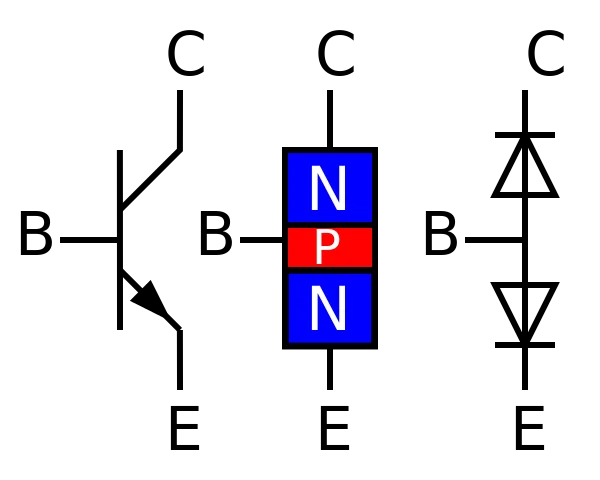
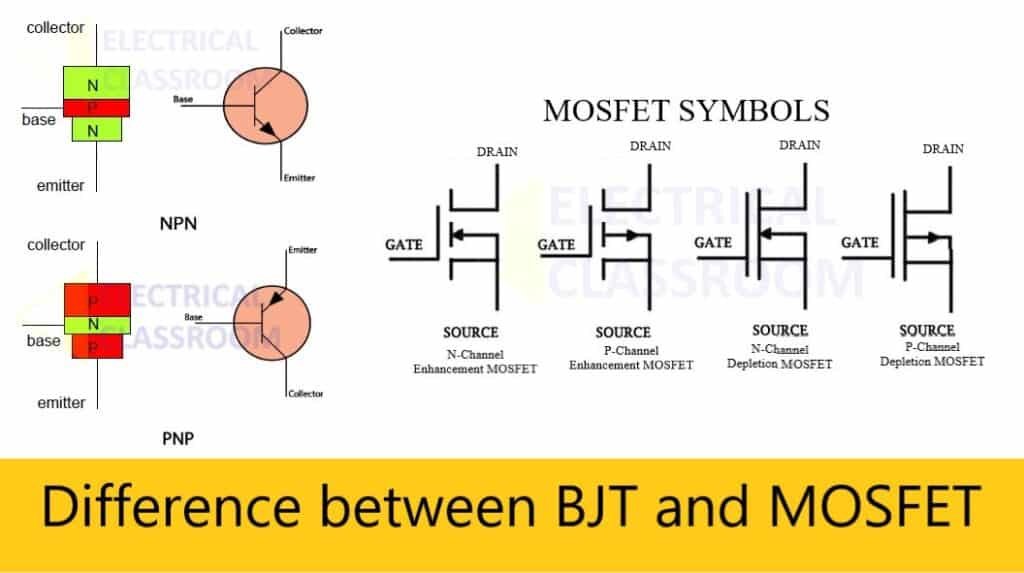
A Bipolar junction transistor, commonly known as BJT, by its construction, looks like two p-n junction diodes connected back to back. It is a three-terminal (Emitter, Base, collector), current controlled device. Based on construction, bipolar junction transistors are classified into NPN and PNP transistors.
In NPN transistors, a thin layer of p-type semiconductor is sandwiched between two n-type semiconductors whereas, in PNP transistors, a thin layer of n-type semiconductor is sandwiched between two p-type semiconductors.
They are widely used as an amplifier, switch or oscillator. It is a current-controlled device, meaning that the amount of current flow between the emitter and collector is controlled by the base current.
MOSFET – Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors
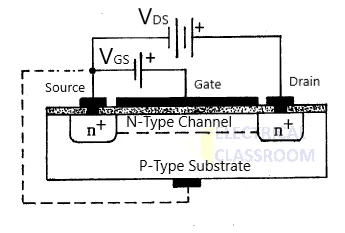
A Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, commonly known as MOSFET is a field effect transistor mostly made from silicon semiconductor material. It is the most used type of transistor. It has three terminals: Source, Gate and Drain. It has metal terminals at the top, a silicon oxide layer beneath the terminals and semiconductor material forming the bottom layer – making it a Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
Based on the operation principle it is classified into Enhancement MOSFET and depletion MOSFET. An Enhancement MOSFET stay OFF under normal conditions and requires a Gate voltage to turn it ON whereas the depletion MOSFET stays ON under normal conditions and requires s Gate voltage to turn it OFF.
Difference between BJT and MOSFET
| Properties | Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) | Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFET) |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | There are two types of bipolar junction transistors: NPN and PNP. | MOSFETs are categorized into enhancement MOSFET (p channel and n channel) and depletion MOSFET (p channel and n channel). |
| Terminals | Base, emitter and collector | Gate, source and drain |
| Symbol | 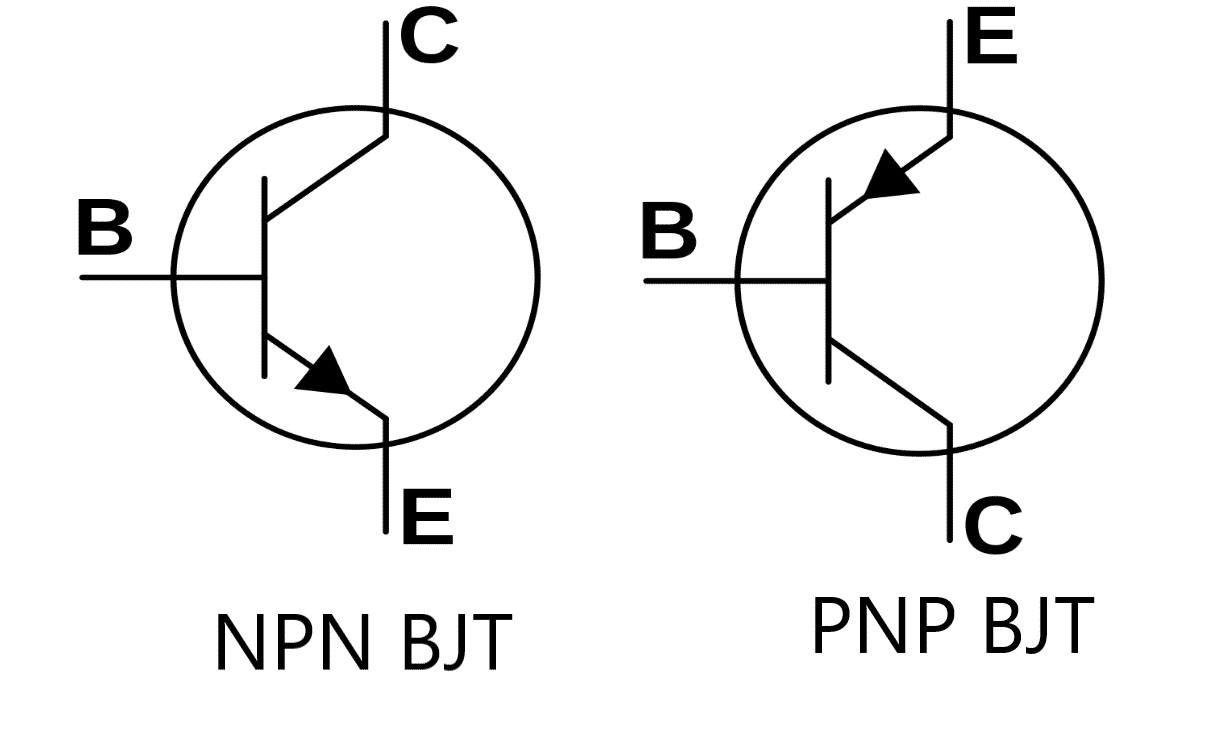 |  |
| Transistor type | Bipolar transistor | Unipolar transistor |
| Charge carriers | Both electrons and holes acts as charge carries in BJT. | Either electrons or holes acts as charge carrier. |
| Control method | A BJT is a currect controlled device. | A MOSFET is a voltage controlled device. |
| Switching speed | The maximum switch speed of a bipolar junction transistor is close to 100KHz. | The maximum switching frequency is 300KHz. |
| Input Impedance | Low | High |
| Output Impedance | Low | Medium |
| Temperature coefficient and paralleling | BJTs have negative temperature coefficient that limits their parallel operation. | MOSFETs have positive temperature coefficient and can be easily paralleled. |
| Power consumption | Since BJT is a current controlled device, it consumes more power than voltage-controlled devices like MOSFET. | A MOSFET Consumes less power than a BJT. |
| Second breakdown limit | A BJT has a second breakdown limit. | A MOSFET has a safe operating area similar to BJT but does not have a second breakdown limit. |
| Applications | BJTs are much suitable for amplifiers, oscillators and switching of circuits with constant current flow. | MOSFETs are suitable for power supplies and high-frequency low voltage applications. |
Review – BJT vs MOSFET
- BJT and MOSFET are semiconductor devices with a wide range of applications.
- BJTs are bipolar devices whereas MOSFETs are unipolar devices.
- A BJT is a current controlled device whereas a MOSFET is a voltage control device.
- The switching speed limits of a BJT is higher than that of a MOSFET
- Both BJT and MOSFET has a wide range of applications. Several factors such as switching speed, control method, power consumption, load type, efficiency and cost need to be considered during selection of proper device.
- View datasheets of BJT and MOSFET.