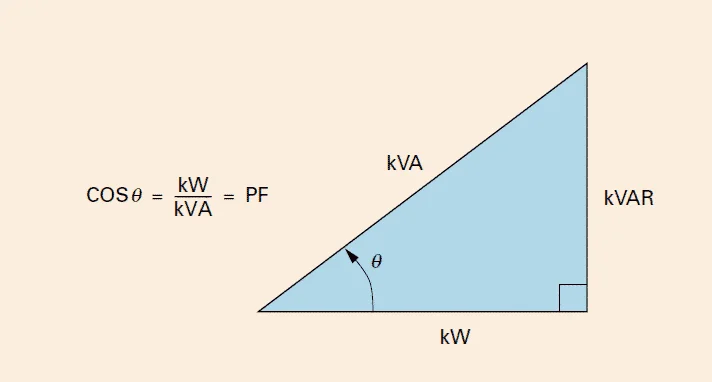
kVA stands for kilo volt-amperes. It is basically the unit of apparent power and is the product of RMS values of voltage and current. One kVA is 1000 volt – amperes
Apparent power
Apparent power is the actual amount of power drawn from the source. It includes both true power and reactive power. Apparent power is denoted as S.
In the case of DC, the apparent power is irrelevant. But when it comes to AC, for reactive loads, the current and voltage are out of phase. So, the actual usable power (true power) depends on the power factor and is always less than the apparent power.
Read more: Real, Reactive, Complex, and Apparent power
AC power sources such as alternators, inverters, and transformers are rated in kVA. The reason behind that is, the output of these devices is independent of the power factor of the load.
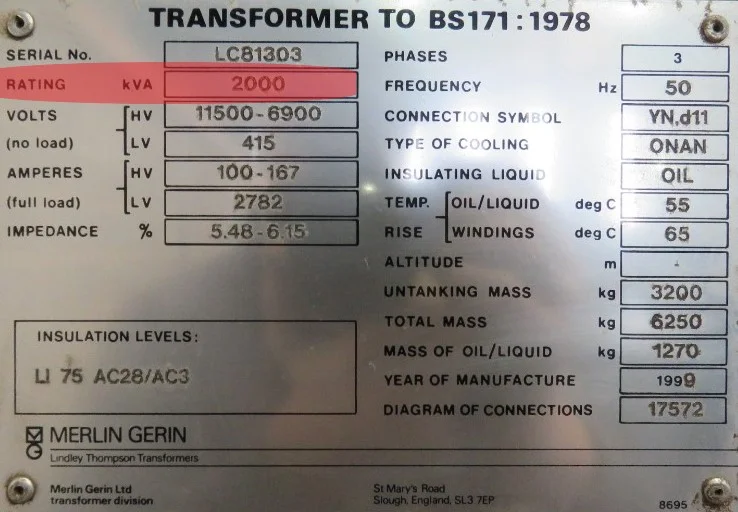
Calculation of kVA – Apparent power
For a single phase, apparent power can be calculated using the following formula.
Apparent power = (Voltage X Current)/1000
For three-phase, apparent power can be calculated using the following formula.
Apparent power = (√3 X Voltage X Current)/1000
= (1.732 X Voltage X Current)/1000
Calculation of current
For a single phase, the current can be calculated from apparent power (S) using the following formula.
Single phase current = (S X 1000) / Voltage
For three-phase, current can be calculated from the apparent power (S) using the following formula.
Three-phase current,
Current = (S X 1000) / ( √3 X Voltage)
= (S X 1000) / ( 1.732 X Voltage)
Where S is the apparent power rated in kilo volt-amperes.
Summing up
- kVA is the unit of measure of Apparent power.
- One kVA is equal to 1000VA.
- It is calculated by multiplying the RMS value of voltage by the RMS value of current and dividing the product by 1000.
- In the case of DC, kVA = kW.
- It is independent of the power factor of a load.
- Alternators, transformers, power supplies, and UPS are rated in kVA.